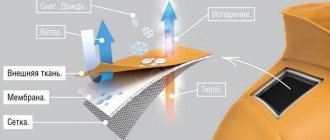
Polycotton is a textile material woven from two types of raw materials: cotton and synthetic. Such fabrics are called mixed or mixed. The idea of using natural and chemical fibers simultaneously was implemented in the production of knitwear back in the middle of the last century. In the textile industry, they have learned to use synthetic and cotton fibers and threads in one product in recent decades.
Background of the issue
This is how cotton grows
Cotton plant is the oldest plant used by humans for domestic purposes. India is considered the birthplace of cotton. Although, as often happens, during the same historical period, cotton began to be used in other southern countries, regardless of India. Cotton fabrics have been at the peak of popularity for thousands of years. It turns out that not only silk was transported along the Great Silk Road, but also cotton, cotton fibers, and fabrics.
Today, there are trends towards reducing the use of cotton fibers in the textile industry.
- In the world, by the beginning of the 21st century, the share of cotton used as textile raw materials decreased and amounted to 35%. The volume of use of synthetic, artificial, and other natural polymers has increased. The pursued goal was to reduce the cost of the product while maintaining its quality.
- In our country in the 60s of the last century, cotton was used 8 times more than other natural fibers. By the end of the century, due to government changes, cotton for Russia became a completely imported raw material. In the 17th century, they tried to grow cotton in the Moscow region, but the attempt failed. The need to import cotton fibers from near and far abroad countries has led to an increase in cost. In neighboring countries, the environmental situation has deteriorated, which has affected the quality of raw materials.
The combination of all circumstances became an incentive for the introduction of innovations in textile production technology.
Photo
Photo #1 Istanbul
Photo No. 2 Tenderness
Photo #3 Loving you
Photo No. 4 Camellia
Photo No. 5 Stripes
Photo No. 6 Coral
Composition of polycotton fabrics
The literal translation of the name of the group of fabrics means “a lot of cotton.” This is true in half the cases.
- If the material is 50% or 65% cotton, and the rest is polyester, then this is really a lot.
- When the cotton content is 15% or 35%, the name becomes conditional.
The rest of the raw materials in polycotton are polyesters (polyesters).
Polyester fiber is made by polymerization (chemical cross-linking) of two repeating components:
- terephthalic acid – an aromatic dicarboxylic acid;
- ethylene glycol - organic dihydric alcohol.
The resulting polymer is widely used for the production of textile fabrics (75%), food films, and packaging (13%). High-quality, purified polyester is absolutely inert and safe.
Production methods, polycotton structure
There are two main methods for producing mixed textile materials. Both are used in the production of polycotton.
- In one case, different fibers in a given ratio are included in the composition of one textile thread. When weaving such textile threads, a homogeneous double-sided material is obtained that combines the qualities of the original raw material.
- In the second case, threads made from cotton are intertwined with threads made from polyester fiber. It is possible to weave one homogeneous thread with a second heterogeneous one, which consists of two different fibers. Depending on the type of weaving, you may end up with a double-sided fabric, with predominantly cotton on one side and synthetic material on the other.
The good consumer properties of mixed fabrics during the production process can be improved by additional processing: application of impregnations and coatings.
The structure of the cotton fibers used depends on the degree of maturity and plant variety. Cotton fibers are:
- short-fiber with a length of up to 26 mm;
- medium-fiber with a length of up to 34 mm;
- fine-fiber with a length of up to 50 mm.
The name of the latter apparently implies that if the fiber is thin, then it is necessarily long. Sometimes it is called that - long-fiber.
The structure of mixed fabric - polycotton - depends to a very large extent on the type of cotton fiber used in the production and the type of threads obtained.
Important properties of threads include:
- thickness (linear density);
- twist (degree of twist);
- breaking load;
- breaking elongation;
- uniformity of all previous indicators.
The variety of raw materials used, thread properties, and types of weaves explains the wide range of products. The average consumer is sometimes perplexed by the many differences in fabrics offered under the same name.
Application
Bedding is mainly used to make bedding: sheets, pillowcases, duvet covers, mattress covers, pillows. However, it is also used in the production of sportswear.
In this case, such a quality as hygroscopicity is especially important, since during intense physical activity the body must breathe. Therefore, when choosing a product, it is necessary to ensure that there is a high percentage of natural ingredients.
Types of weaves used in the production of polycottons
When making polycotton, simple (main) types of weaves are used.
- Linen. Plain weave, in which each warp thread is intertwined with each weft thread through a single thread, results in a reversible fabric with smooth surfaces. This is how they do chintz, calico, calico, cambric.
- Twill. In a twill weave, the weft thread covers 2 or 3 warp threads, diving under the next warp thread. Weaving is done with a shift in one thread. The result is a reversible fabric with a smooth, slightly shiny face, on which diagonal ribs are barely visible. Such fabrics are softer than linen and do not wrinkle as easily, but may have less strength.
- Satin. With satin weaving, at least 4 warp threads under the next 1 warp thread are covered with a weft thread with a shift of at least 2. The result is a double-sided fabric, smooth and shiny on the front side. The resulting soft material has a slightly slippery surface on one side. It may crumble at the edges.
The type of weave determines the properties and purposes of the fabrics.
Properties
Polycotton, the composition of which is optimally selected, is pleasant to the touch and durable. It does not deform even after numerous washes and does not lose its original color. Polycotton practically does not wrinkle, so does not require ironing.
Author:
Anastasia Kukushkina
I hope you enjoy the article I have prepared for you! If you find errors in it, write to me about it! I will answer any questions you have, ask them!