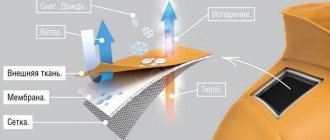
Membrane fabric: does not allow water to pass through, but allows breathing.
The development of fabric production technologies has made it possible to obtain a new generation of multifunctional materials. One of them is a membrane - a semi-permeable film with a special structure. Multilayer fabrics that include such a film are called membrane fabrics; in finished products they do not allow water to pass through from the outside, but allow the moisture that forms inside to evaporate. The bottom layer is soft, the top layer is protective and wear-resistant. The middle one is a protective fabric and membrane.
The first membrane was produced in 1969 by Wilbert L. Gore and Robert W. Gore. It was intended for use in space, the name was patented as Gore-Tex. It is made from fluoroplastic (Teflon). After the patent expired, other similar materials appeared that are used for the production of workwear and footwear. For example, synthetic fabric “alova”, which consists of 100% knitted polyester on the outside and a membrane on the inside.
History of membrane fabrics
The first membrane was produced in 1969 by Wilbert L. Gore and Robert W. Gore. It was intended for use in space, the name was patented as Gore-Tex. It is made from fluoroplastic (Teflon). Since the patent expired, other similar waterproof clothing materials have emerged and are used to make workwear and footwear. For example, synthetic fabric “alova”, which consists of 100% knitted polyester on the outside and a membrane on the inside.
Recommendations for selection and use
The choice of material directly depends on the purpose of use.
In order for the canvas to last a long time, it is necessary to take into account a considerable number of factors when choosing.
- Density - the denser the material, the worse it allows moisture and air to pass through. If agrofibre is purchased for mulching or preserving heat in the soil, choose spunbond that is quite dense - 60 g/m². To prevent sunburn and protect against birds, choose a thin fabric with a density of 12–30 g/m² so that the fabric does not crush the sprouts.
- Additional modifications - lamination, spot coating - change the properties of the material. This needs to be taken into account. Reinforced fiber is completely unsuitable for protecting plants from the sun, and material with PVC spot coating is not suitable for a drainage system.
- You need to choose quality material . The only indicator can be the manufacturer’s warranty and its reputation. The only visible sign of quality is the homogeneity of the material. If there are gaps or compacted areas in the canvas, it is a counterfeit.
- Spunbond is produced with and without UV protection . The first option is used for gardening and façade windproofing. Unprotected material is used inside the building.
Thin spunbond cannot be washed.
Some spunbond products require care , especially for clothing covers, bags and clothing with lining. The rules are simple:
- Items made from spunbond cannot be washed ; thin fabric cannot bear such a load. Hand wash allowed, very gentle and without powder or soap.
- Preference is given to dry cleaning : it is better to vacuum the product or wipe with a dry sponge.
- Do not iron the material. Clothes with such a lining are ironed only on the outside or use a steam generator.
Disposable products are thrown away after use.
Advantages
The main properties of the fabric are:
- waterproof. Expressed in numerical equivalent. It indicates the water pressure that the fabric will withstand. There are various indicators that you should pay attention to when purchasing such products: the number 3,000 means that the fabric can withstand light rain and light snow, 10,000 - heavy rain, 20,000 - the fabric will not get wet in severe bad weather and stormy conditions;
- vapor release. It is also expressed in a numerical equivalent - the amount of steam in grams per square meter of fabric that it produces per day. The higher the indicator, the better the fabric;
- wind protection.
Main characteristics
The properties of a material largely depend on its density and structure. The main characteristics include the following.
- Hygienic – spunbond does not form toxic compounds when exposed to the external environment.
- Operating temperature range – -55–+130°С. At high temperatures, the fibers begin to soften and then melt.
- High elastic properties - even after prolonged creasing, it restores and retains its original shape.
- Non-woven material can be easily dyed in any color . Coloring occurs during manufacturing: dyes are added to the raw materials.
The fabric is not only elastic, but also soft. Spunbond is often used to cover greenhouses or greenhouses. It is much cheaper than glass or polycarbonate. It retains heat just as well.
Density
Variable from 10 g/m² to 600 g/m². This parameter defines the destination. Spunbond with a density of 40 g/m² is used for sewing disposable clothing, and with a density of 200 g/m² it is used as an agrotextile fabric.
Dimensions
The thickness of the material determines its some parameters - water permeability, rigidity, ability to retain heat. The width of the web varies from 6 cm to 4 m. As a rule, spunbond during production is cut according to the customer’s wishes.
The length of the fabric in a roll can reach 1500 m.
Melting temperature
The parameter depends on the nature of the polymer used. When heated, the fibers first soften and the fabric stretches. At high temperatures, matter begins to melt. The process takes a lot of time and occurs gradually, so it is impossible to talk about the exact melting point.
Deformation of the most heat-resistant material - based on polypropylene - begins at a temperature of +130°C .
Kinds
Read about: mesh fabric: an overview of a wide range of applications.
The membrane is produced from organic and inorganic materials. There are several types:
- porous (Teflon). It has micropores on the surface of the outer layer, which do not allow water to pass through, but allow the moisture that collects inside to evaporate freely (diffusion of molecules). The disadvantage is that the pores can become clogged, and then the evaporation system is disrupted;
- pore-free (polyurethane). It has no pores on the surface and does not allow water to pass through. The moisture that forms inside the product first accumulates on the inner surface of the outer layer, then gradually evaporates. The disadvantage is that the moisture does not evaporate immediately, and the product may feel wet;
polyurethane membrane
- combined. Inside this material there is a pore membrane, and on top of it there is another protective layer that protects the pores from clogging. This type of fabric combines the advantages of the first two.
Structure
According to their structure, membrane tissues are divided into:
- two-layer. In such a fabric, the membrane and the outer surface are connected, the lining is not fixed. It breathes well, is flexible and relatively inexpensive;
- three-layer. The top layer is glued to the membrane and lining (mesh). This material turns out to be lighter, less air permeable, it is called laminated fabric. Its price is the highest;
- membrane in 2.5 layers. Instead of a liner or mesh, a foam padding is used to protect the membrane.
Application of membrane fabric
Read about: tarpaulin fabric: a composite of a cotton base and rubber.
Now this material is used to produce clothing and shoes for people leading an active lifestyle. Jackets, trousers, overalls, tracksuits and shoes are made from it. This is an indispensable material for climbers, athletes, tourists, and people involved in extreme sports. In recent years, children's outerwear has also been made from it.
Since the membrane itself does not protect against the cold, clothes made from it can be demi-season and have insulation (fleece). Jackets and overalls made of membrane fabric can be painted in a wide variety of shades; camouflage colors are also very popular.
Benefit
In addition to excellent hygienic and protective properties, clothing with a membrane is valued for:
- ease;
- strength;
- convenience;
- bright colors.
The disadvantage of such clothing can be its high cost, as well as its fragility if care rules are not followed.
How to wear
The basic rule for wearing clothes with a membrane is layering. You need to wear a bottom layer (underwear), a middle layer (sweater) and a membrane. At the same time, it is better if the inner clothing contains a certain amount of synthetics in order to allow evaporation to pass through.
How to care
Membrane clothing cannot be washed with ordinary powders, as they can damage the structure and clog pores.
- You need to use special detergents, laundry or liquid soap. Do not spin in the washing machine. When hand washing, do not twist the product too much. If there are heavy stains, they can be removed with a soft brush.
- After washing, the water should be allowed to drain, then hang the item outdoors or in a room away from heating appliances and away from direct sunlight.
- During the production of clothing, a special DWR (Durable Water Repellence) coating is applied to its surface, which provides it with additional protection from moisture. After repeated washings, this coating disappears, so it is recommended to restore it each time after washing using a special spray. This coating is sprayed onto a dry, clean surface.
- Membrane clothing cannot be ironed, as contact with a heated iron will damage its structure.
Shoes
The membrane is located in the shoe in the form of a sock, usually does not reach the very top. Its location also depends on the design of the shoe itself, the presence of a zipper or tongue. A special microclimate is created in the boot; evaporation from the human body passes through the membrane and comes out due to the difference in internal and external pressure. The top of the shoes is usually protected with waterproof and wear-resistant fabric.
On a note
Just like with outerwear, the principle of multi-layering works here - you need to wear socks under membrane shoes. They should not be 100% cotton or wool, but contain at least 10% synthetics. Then the steam will be released.
If water gets through the top layer, the membrane will not let it through, but the water will remain in the shoes. Therefore, it is very important to dry it well.
Shoe care
- Do not allow dirt to stick to the surface, as the pores must be open.
- Membrane shoes should be cleaned with a dry brush or sponge dipped in soapy water.
- Dry away from radiators and other heat sources; you can put newspaper inside.
- Every time after cleaning your shoes, it is advisable to treat them with water-repellent sprays.
Industry
In the production of various machine instruments, pumps, carburetors, etc. a rubberized membrane is used. This is a technical fabric, vulcanized on both sides.
Protective covers and upholstery for furniture are sewn from synthetic aloe.
High-tech membranes for clothing destroy all the old ideas about a warm, waterproof product: it is not heavy, it is comfortable for both adults and children, and has excellent aesthetic qualities. And with proper use and proper care, products made from membrane fabric will last a very long time.
© 2021 textiletrend.ru
Types of spunbond
Laminated
Two-layer material with polypropylene coating. This modification creates a fabric with greater strength and rigidity at a low density - from 42 to 65 g/m². It is slightly permeable to moisture and air and has a water-repellent effect. Polypropylene protects against the absorption of oil, dirt, and other biological fluids. The fabric is often used to make clothing for medical staff and is used for other medical purposes.
Color
Spunbond is easy to paint if done at the initial stage. Any shades . Color does not affect the physical and chemical characteristics; this is a purely decorative technique. Covers are often made from spunbond, and the interior lining of bags and furniture is made, so the material is also produced with a pattern.
Shade is taken into account when choosing in gardening. White material reflects sunlight, so it is used for arranging a greenhouse. Black agrofibre absorbs light and transmits it to the ground, so black spunbond is used as a covering material on the soil.
Reinforced
Non-woven fabric intended for covering greenhouses and greenhouses. Spunbond is strengthened with synthetic fibers . The fabric is strong but flexible. Reinforcement significantly increases the wear resistance of spunbond and sensitivity to sunlight.
Reinforced fabric is often laminated to ensure water resistance.
Foil
The material has a backing made of a thin layer of aluminum - foil . This spunbond is waterproof and very durable with the same flexibility. This option practically does not burn. The canvas is used as waterproofing in a bathhouse, in a sauna, on a balcony, as a vapor barrier film when working with external walls.
PVC spot coated
The material is reinforced not with fibers, but with pinpoint portions of polyvinyl chloride. The fabric is durable, very dense, non-slippery. Spunbond is a smooth material that slides off easily without fastening. The spot coating option is held to the surface.
Spot coating increases tear resistance.
Filtering
The fabric of low density and without an amplifier acts as a universal filter material. It does not absorb water, but allows it to pass through. This quality is used in the construction of a wide variety of drainage and filter systems.
Geotextile is one of the spunbond options. It is used to retain water in garden beds.