A light and dense twill weave fabric made from the down of a special breed of mountain goats is cashmere. These animals are found in the foothills of China, Pakistan and India. The wool yarn takes its name from the province located on the border of India and Pakistan. Dresses, skirts, trousers, coats, jackets for women and children - that's it. What is most often made from cashmere.
This fabric is characterized by its weightlessness, it is pleasant to the touch, and does not cause allergic reactions. The thickness of human hair is on average 4 times the thickness of the wool fiber of cashmere goats. The fluff is carefully combed out during the molting season, washed, straightened, combed, twisted into the finest yarn, which is then intertwined in a special way, transformed into a thin durable material - cashmere fabric. Approximately 150-200 grams of fluff are combed from one goat per year. Therefore, to make a dress from cashmere yarn or a pullover, the down of 6-7 animals is needed.
Cashmere became popular in Europe at the beginning of the 18th century; robes for kings and court nobility were made from this expensive material. Pleasant to the touch, lightweight, but protecting from the cold, cashmere has not lost its popularity over 300 years. On the contrary, the number of its fans is constantly growing, which forces many fashion houses to replenish their collections with cashmere products. It is not enough for a person to just feel warm; he strives to surround himself with gentle and comfortable warmth, and this is clothes made of cashmere fabric and knitwear.
Variety of species
According to its composition, drape is:
- Elite - the highest grade. It is obtained by double weaving fibers from 100% selected woven wool. The fabric has increased wear resistance and retains its original appearance for a long time.
- Pure wool fabric allows the inclusion of no more than 15% impurities. These can be chemically recovered wool fibers. Made from high-grade raw materials using double-sided weaving.
- Fabrics from the cheap category are made from low quality threads in the bottom layer. The underside of them looks looser and more fibrous. It is difficult to find external differences from expensive options, but the density of such drape is less and it is ventilated in bad weather.
- Material containing 30-85% wool is considered to be wool blend. During production, several percent of viscose, polyester and nylon fibers are added to the weaving of the lining layer. Mixed drape is easily distinguished by its looseness and softness.
- A synthetic drape in which a combination of polyester and artificial threads manages to achieve an external resemblance to its wool counterpart. A cheap substitute is used in toys, workwear and souvenirs.
According to the dyeing method, the fabric is classified:
- Threads of the same color make it possible to obtain a plain, plain-dyed fabric.
- The use of two or more tones gives a melange drape, for example, “houndstooth” as in the photo. Intricate and skillful weaving increases the value of the fabric.
- Multi-colored or variegated drape is obtained by weaving with multi-colored threads.
Changing the technology of pile processing produces the following types of material:
- Unlined with a smooth surface.
- Ratin - with a diagonal arrangement of the pile in narrow stripes.
- Fluffy on the front side, due to the addition of goat fluff to the two-layer fabric.
- The fabric is machine pressed and brushed, which makes the weave structure invisible. The result is a fluffy or smooth velor drape with thick and soft pile.
- bottle, when an intricate pattern is formed from the pile.
The thickness of the finished canvas may vary. Accordingly, the drape is produced:
- single-layer with satin or twill weave threads. Belongs to the category of costume fabrics. Its density is limited to 550 g/m².
- one and a half layer 600 g/m². Demi-season coats are made from it.
- Two-layer, up to 700 g/m². It is intended for winter combined warm products.
Classification of coat fabrics
Many materials are used to sew coats. They differ in the composition of raw materials, weaving method, density and dyeing methods. To understand the variety of fabrics, they are classified according to the most important characteristics.
Density
For summer, demi-season or winter coats, fabrics with a certain density are used, which should not exceed the maximum permissible standards:
- for men’s – no more than 650g/m2;
- for women’s – no more than 500g/m2;
- for children - no more than 360g/m2.
Weave type
The appearance of the material and its main characteristics largely depend on the method of joining the fibers. The most common weaves used in coat fabrics are:
- linen;
- twill;
- jacquard;
- finely patterned;
- combined.
In addition, some canvases use a special pile weave. In this way, for example, corduroy reps and corduroy ribbed are obtained.
Coloring and patterns
Coat materials can be plain-dyed, variegated and melange. At the same time, all manufacturers try to use stable dyes that do not fade or fade in the sun.
Various patterns and prints – images printed on the fabric – help to attract attention to the product and emphasize its attractiveness. The most fashionable at present are:
- herringbone or broken strip;
- "chicken foot";
- tiger-leopard colors;
- geometric;
- abstraction.
Two- or multi-color stripes and checks will always be in trend. For women's summer coats, floral motifs are often chosen, and for children's coats, prints with fairy tale or cartoon characters are chosen.
Important fact! For colorful and iridescent coats, you should choose only monochromatic accessories - shoes, a handbag, a hat or a scarf. Otherwise, the image will be too “flashy” and may serve as an object of ridicule.
Raw material type
The level of thermal insulation is one of the most important characteristics for coat fabrics. This indicator is directly related to the type of fibers from which they are created.
Based on the type of raw material, all fabrics for sewing coats are divided into wool and cotton. The first, in turn, have the following subgroups:
- worsted;
- fine cloth;
- rough cloth.
Only after familiarizing yourself with the basic characteristics of materials and studying how to care for them can you make the right choice. Let's take a brief look at the most common coat fabrics.
What type of fabric is this
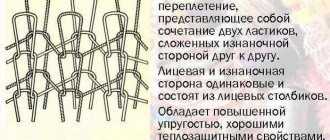
Drape is a thick woolen or wool-blend fabric made from cloth-spun yarn with a smooth front side and a fleecy back.
What colors does drape come in?
Its production became possible after the invention of special weaving machines that made it possible to produce material in which the threads are arranged in several rows, i.e. have 1.5 or 2 layers of weave. The fabric consists of two layers, so it has increased heat-insulating properties. As a rule, the front side is made from higher quality wool.
What purposes can this fabric be used for?
Depending on the composition of the drape, its density, degree of hairiness, the purposes of its use also differ.
Suits, skirts and trousers are made from thin drape velor
From soft fluffy drape moth - hats and women's coats
Men's coats and ceremonial overcoats for senior officers are sewn from drape-castor, a dense, heavy material.
Coats for men and women, winter and demi-season, are made from drapery fabric, thick fabric.
Soft toys, bags, and workwear are made from synthetic drape.
Description
The drape is a dense, multi-layered fabric with high thermal insulation and protection from wind and bad weather. The density of the material is created by one-and-a-half or double woven connection of threads and subsequent hardware pressing.
This material is heavy and holds its shape. It does not wrinkle when worn and gives the figure a slender and elegant silhouette. The composition of the drape is natural wool, which is nature’s warmest material.
What are they sewing?
Drape is a fabric that is widely used for making suits in classic and modern styles, sophisticated and warm coats, original hats, caps and scarves. Blended fabrics are used for windproof equipment and uniforms.
The material is universal, easy to use, easy to cut and sew. The slices do not crumble at all.
Accessories, decor and toys are made from drape. It is in demand in interior design and furniture production for covering sofas and armchairs.
History and geography of cashmere
Napoleon was the first to bring cashmere to Europe; he gave Josephine an excellent shawl made of high quality cashmere - pashmina. Cashmere is expensive not because of the whim of its manufacturers, but because it is quite difficult to obtain. After all, fluff is collected (combed or plucked from mountain goats) once a year, after the animals have overwintered, when the goats no longer need it. Before the onset of the next cold weather, the animals will have time to acquire a new undercoat, which will protect them from the severe frosts in the Himalayas. Thus, unlike leather and animal fur, cashmere is also considered the most humane natural material.
Today, the Chinese are rightfully considered the best producers of cashmere fabric. Mongolia is firmly in second place, producing about 28% of all cashmere produced in the world. The geographical location and existing climatic conditions of Mongolia are ideal for living and breeding goats that supply fluff for cashmere. It is in the harsh and dry climate of this country that goats thrive. Milder climatic conditions lead to the loss of that special undercoat that goes into the production of high-quality cashmere.
In addition to China and Mongolia, cashmere is produced in Iran, New Zealand, Afghanistan, Nepal, the USA and Australia.
Care instructions
Any thing requires care, and drapery requires special careful treatment. Some tips:
- If you get caught in rain or sleet, do not put the item in the closet, hang the coat on a hanger and let it dry.
- If the product is too wet, lay it out on a dry towel and then hang it on a trempel.
- Stains and dirt are best removed by dry cleaning.
Some drape items can be washed in a washing machine. How to care for them, what mode and temperature to set, can be found on the manufacturer’s label. Do not set high temperatures or rub the product.
What standards are used in production?
All standards for the production of woolen fabrics, including drapes, are indicated in GOST 28000-2004: Pure wool, wool and half-woolen clothing fabrics. General technical conditions".
Options:
- grade - GOST 358-82;
- resistance to moth damage - GOST 9.055-75;
- density of threads and pile bundles - GOST 3812-72;
- standards of hygroscopic and water-repellent properties - GOST 3816-81;
- color fastness to washing - GOST 9733.4-83;
- abrasion resistance - GOST 9913-90;
- creasing - GOST 18117-80;
- change in size after chemical washing - GOST 30157.1-95.
How to distinguish cashmere from a fake
Buyers often have questions about how not to make a mistake and choose high-quality cashmere, how to determine how real it is.
- Natural cashmere is lightweight and the cuts look slightly uneven.
- The fabric has a characteristic smoky shade.
- Goat down fibers are distributed naturally, unevenly, while on synthetic analogues, fibers of the same thickness are arranged evenly, “one to one.”
- Real cashmere without the addition of silk does not shine (the maximum allowable presence of silk threads is 30%).
- The fabric does not electrify and does not attract dust.
- When compressed, cashmere drapes softly and silently, while synthetic analogues can emit a characteristic “creaking” and cause unpleasant tactile sensations.
- When the threads are set on fire, the down fabric burns completely, crumbles in the hands and emits an unpleasant odor of organic origin. Synthetics do not burn, but melt, filling the space with the specific smell of plastic.
Requirements for coat materials
A coat, as a rule, is bought or sewn for more than one season, so it is very important that the material for it is not only beautiful, but also has the following quality indicators:
- high level of thermal insulation;
- durability;
- lack of peelability;
- color fastness;
- resistance to stretching and shrinkage;
- ease of care.
Recently, the fashion for summer coats has resumed. The fabrics from which they are sewn must conduct air well and not “float” the body, and also be waterproof and resistant to stains.
Properties
Products made from drape have excellent characteristics, because it is not for nothing that they have been loved for several generations:
- Density and ability to retain heat;
- provide air access to the body;
- give comfort and coziness;
- in an open space, foreign odors from tobacco, mothballs or sweat quickly disappear;
- reliably protect from wind and cold;
- clothes are wear-resistant and durable;
- easy care and practicality;
- versatility - products are suitable for everyday life and holidays;
- elegant and attractive appearance.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pros:
- has high heat-insulating properties;
- able to maintain the shape of products;
- practical;
- easy to care for;
- does not cause trouble in cutting and sewing;
- long service life;
- Versatile: suitable for sewing everyday items and high-end clothing.
Minuses:
- the most important thing: moths “love” this fabric very much;
- soft drape is difficult to smooth out;
- high price (for pure wool).
Other types of fabrics for coats
For sewing, you can use pile fabric consisting of a large number of vertical threads. This coating is created from different materials.
For example, faux fur and corduroy. This option retains heat even at low temperatures. It is strong and durable, and also protects well from the wind. herringbone print often adorns drape, wool or tweed. The pattern is obtained from a weave of contrasting and dense threads. This fabric is famous for its wear resistance and durability. The raincoat contains cotton and synthetic threads.
A type of varnish is used to sew coats. Raincoat fabric produces wear-resistant products that tolerate moisture well. Wear-resistant options include jacquard , which is created from the interweaving of weft and warp fibers.
Varieties
Manufacturers offer different types of drapery materials, they differ:
- Appearance – lint-free, with lint, with a fluffy coating, satin.
- Composition: pure wool, half-woolen.
- Density – fine cloth, coarse cloth.
- Lightweight and heavy.
- Degree of coloring – plain-dyed, multi-colored.
Military overcoat cloth is produced; it requires special production technology. The fabric has increased wear-resistant properties: increased density, is not afraid of sparks, like nettle fabric, does not allow wind to pass through, does not get wet, and does not wrinkle.
Elite - what properties and abilities do fabric products have?
This type of cloth is made from merino wool. It contains: wool, cashmere, polyester. This fabric is often called “cashmere”. Velor thread is loose and especially soft. Coat fabric made of drape velor has a front and back side and is distinguished by a satin weave. The front side is softer and velvety to the touch, with low-cut pile. The material is elastic and has improved performance qualities. Used for sewing coats, short coats, and warm jackets. Find out how to glue dublerin and how it differs from non-woven fabric here.
The most expensive material is drape velor.
Pure wool
Natural fabrics are made from alpaca or less expensive sheep wool. The composition of pure wool fabric may vary. Both 100% wool fabrics and a small admixture of recovered wool thread are produced. The fabric, like the two-thread footer, has a double-sided weave, both surfaces look the same. In the Soviet years, when there was a shortage of beautiful clothes and high-quality fabrics, drapery products were given a second “life” by re-facing things. If you have sewing skills, you could do this yourself at home or take the coat to a fashion studio.
Synthetic
Among the varieties of cloth is synthetic drape, which outwardly imitates woolen drape. This material is used in the production of toys, home textiles, for sewing cheap clothes, and souvenirs. The edges of the material do not crumble and are easily glued together with PVA glue. This property allows you to create various applications and the smallest details. Synthetic drape is a godsend for needlewomen:
- You can decorate your interior with products made from this fabric;
- update furniture;
- sew rugs or warm pillows for chairs, various napkins.
Melange
Drape melange is made from fibers of different colors. This mixture of colors gives the fabric a melange effect. The material differs from dyed fabrics and is quite expensive. Outwardly, it is similar to tweed, but denser and thicker. The famous houndstooth suits in the style of the famous Chanel still do not leave the catwalks. Coats, winter jackets, women's two-piece suits (jacket and skirt) are made from melange tweed, and men's short coats are made from dark herringbone.
The most common pattern, which has not gone out of fashion for many decades, is the “houndstooth” and “herringbone”.
Unlinted
Smooth, lint-free drape is produced using general technology. It is simple to cut; if fleecy material must be laid out exactly in the direction of the pile, then these requirements do not apply to smooth material. Also, non-lint fabric is easy to care for and more wear-resistant. It does not form pills, and even after prolonged wear, the products have an impeccable appearance. Items made from smooth drape can be ironed using the “Wool” mode. Non-lint fabric is used for sewing overcoats, men's coats, jackets, workwear, and men's caps.
Ratin
Drape-ratin is an expensive material. Its main feature is the presence of obliquely arranged fleecy stripes on the front surface. Pure wool threads are used for production; the twill weave method produces diagonal scars with densely located fibers. To the general technological process for the production of drapery fabric, another processing is added, ratification. The machine is a press with a heated plate; after squeezing, the material acquires the structure of a herringbone or diagonal strip. The fabric is produced in gray and black tones. This article will tell you what you can sew from Pikachu fabric.
bottle
Heavy types of drape fabrics include bottles. It consists of 80% merino wool and 20% sheep wool of the Tsigai sheep breed, which is a fine wool species. Tsigai wool is more like fluff, but it is strong and elastic. The fabric turns out to be dense and harsh, the front side is covered with thick pile. Products made from drapery bottles are wear-resistant, the fibers practically do not fall off. The bottle is used to make men's outerwear. It is not recommended to wash it at home; items with a brushed front should be dry cleaned.
The material requires careful handling.
Fabric composition and its properties
The basis for the production of drape is wool threads. They may be of different origins. The most expensive wool is alpaca (a South American relative of the camel), 7 times warmer than sheep wool. Camel wool is not so expensive, but has high waterproof properties.
The composition and quality of the drape depends on the percentage of wool:
- Pure wool - 90-100% consists of natural wool (in some countries, standards allow 85% wool content). Here the front and back sides are almost the same. A coat or suit made from such drape can be altered.
- Wool blend - the amount of synthetic fibers can reach 70%. As a rule, it is looser and lighter due to the content of nylon or viscose fibers. The more synthetics in the composition, the worse it heats and the shorter its service life.
Alpaca
Alpaca - what kind of fabric is this? Features and rules of fabric care
more details