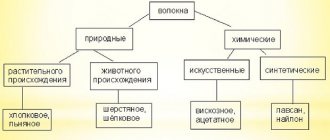
The textile market offers a wide range of materials made from different fibers. But it is natural fabrics, despite the wide choice of solutions, that hold the lead in terms of popularity among buyers. Cotton fabric fibers can be light and dense, and are among the most accessible and widespread. Areas of application: sewing clothes of different categories, bed linen, home textiles, creating furniture upholstery. Various processing methods and weaving threads provide a wide range of cotton fabrics.
What influences the density of cotton: rare, strong
Cotton fabrics are represented by a wide range of strong fabrics based on plant fibers. The raw material is a variety of cotton, the plant from which the fibers of the threads are obtained. Previously, weaving was manual, but now these processes are as automated as possible. Find out how Cotton differs from cotton here.
Table of density of some fabrics.
Taking into account the footage in millimeters of primary raw material, yarn is often divided into short-fiber (up to 27 mm), medium-fiber (range 28-34) and long-fiber (at least 35 mm). Fibers shorter than 20 mm are not suitable for making yarn. The longer the original raw material, the stronger and smoother the fabric will be. From short fibrous structures, loose, fleecy material of heterogeneous thickness is obtained. The bulk of cotton fabrics are made using medium fibers.
Shades of raw cotton - pink, yellow-green, milky white. The threads lend themselves well to dyeing. This material will tell you about cotton rags.
Basics of production, composition
The material is obtained from cotton plant fibers. This is an unpretentious shrub that does not require special maintenance conditions. The main cotton supplying countries are China, USA, India and Pakistan.
To make fabric, the plant is not completely processed - only its “box”, in which the cotton is located, is used. When it ripens, the petals of its capsule open to reveal a white, fluffy substance that is soft. It is collected and processed in a factory to produce threads. First, the fibers are twisted and pressed, and then bleached - cotton is naturally grayish-yellow in color, and it can also become dirty during the collection process.
Dyeing of the material occurs both at the thread processing stage and when the fabric is ready. This is done with synthetic dyes that are safe for humans and resistant to temperatures, detergents and other factors. To add strength to cotton threads, they undergo mercerization (soaking in sodium at 0 °C) before weaving.
When describing cotton fabrics, the characteristic “cotton” is often used. In fact, the material does not contain any paper; this name comes from the foreign origin of the word. The fact is that cotton appeared in Rus' much earlier than paper, and it was brought from Italy, where it was called “bombagio”. Cotton itself is 95% cellulose, with the remaining 5% being minerals and fats.
Polyester may be added to some types of fabrics. This is done to increase strength and add shine to the material. Cotton is also mixed with other natural fibers - linen, viscose.
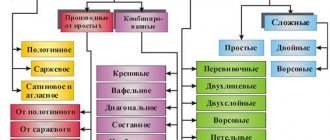
Types of cotton fabric by density
Both the appearance and strength of the material depend on the density of the weave of the threads. Let's look at the main groups.
Thin (light) made of sharply woven threads
The most popular fabric is light, thin chintz. It is obtained as a result of plain weave. It is used in sewing bed sheets, light summer dresses, children's clothing, and shirts. Chintz is weightless, pleasant to the touch, and does not stretch. Find out about the types of chintz at this link.
A more practical plain weave fabric is calico. This is the best choice for sewing bed linen. Batiste is a slightly transparent, delicate cotton fabric made from twisted cotton threads. The material is thin, soft, and has a wide range of applications.
Another interesting example is an interlock obtained by crossing. This is a dense knitwear that is pleasant to the touch with a smooth surface; the back and face look the same. The material is used for the manufacture of men's clothing and tracksuits. Wool fabric is also used for suits and jackets.
Durable rigid with printed pattern
The first example in this group with a printed pattern is poplin. The fabric is produced by thin linen weaves of threads. As a result, a thin scar becomes visible on the surface of the fabric. Very pleasant to the body, soft, but at the same time durable material for sewing everyday clothes and bedding. The ductility of poplin is higher than that of calico, and its durability is better than that of chintz.
Satin, unlike softcotton, has a silky smooth surface with a slight matte sheen. It comes out of double weaves of twisted cotton threads. Flannel is a soft fabric, brushed on one or both sides. Weaving - twill or linen. Flannel is used for sewing casual clothes and soldiers' foot wraps.
Tartan is a fabric with a multi-colored checkered pattern. Dense, durable raw material for sewing kilts, skirts, and school uniforms. For velvet, pile weaving is used, introducing additional threads into the fabric being produced. As a result, a short, soft lint comes out of the face.
Coarse from thick yarn
A dense material with a twill weave, denim has not lost its popularity for thousands of years. Jeans can be used to make clothes for women, men, children for all occasions, outerwear, work clothes, and accessories. This article will tell you everything about denim.
Raincoat, like canvas fabric, is a rough, thick material. It is treated with impregnation with water-repellent properties. The density is high, so is the strength. Raincoat fabric is an excellent option for sewing overalls, jackets, and clothing for active recreation.
Unfinished cotton
Unfinished fabric is also called raw fabric; it comes without dyeing or finishing straight from the loom. An example is cotton wool, soft, warm and dense with twill weaving and brushed on the inside. Twill material comes with threads that intersect by asymmetrical shifting from 1 to 3. There are small protrusions, the fabric is thick, heavy, dense, and abrasion resistant.
Twill is a good lining with stretch and drape. Also pay attention to moleskin - dense textiles of satin weave, smooth, wear-resistant, durable.
Thick (dense)
Plain weave of the thread-over-thread type is suitable for the production of fabrics with smooth, even surfaces. The advantage over other types is its excellent rare strength. Plain weaving is used to make taffeta, poplin, and cambric. Twill is a dense fabric with an asymmetrical shift of threads and an interesting pattern. Matter comes out with indentations, heavy, rough, dense. These are flannel, tartan, cotton wool, denim. Find out how denim fabric is produced here.
Popular dense cotton fabrics:
- rep - dense silk or cotton material, with convex, narrow, parallel scars running from the face;
- the matting is strong and dense, there are checkerboard squares on both sides, the shine is silky, pleasant;
- raincoat fabric - woven fabric treated with impregnation with moisture-repellent properties;
- cloth is a material with twill or plain weave, pre-felt, dense and durable.
Cotton materials of this group are suitable for sewing not only clothes, but also work equipment, furniture upholstery, covers, pillows, and tents.
Properties and characteristics of cotton fabric
The main property of cotton materials, due to which this fabric has become widespread, is that cotton clothing allows the skin to “breathe”. Therefore, such things are significant for allergy sufferers and children, although they are worn by everyone who loves comfort and ease of clothing.
Other positive characteristics of the material are worth noting:
- Durability - even after numerous washes, cotton does not stretch or shrink (if it has been decatified); it is ironed at high temperatures. And you also don’t have to worry that the fabric will tear due to awkward movement - the cotton weave is strong to withstand the impact.
- It is easy to process - sewing from such a flap simply allows the stitches to lie evenly, and the cuts do not fray.
- Hygroscopicity – strongly absorbs water, which is an advantage of cotton when sewing summer clothes and bed linen.
- Remembers the shape after ironing.
- Keeps you warm.
- Inexpensive.
There are few disadvantages, but they also exist:
- It shrinks greatly if the fabric has not been treated before sewing.
- Wrinkles (but can be ironed without problems).
The exact characteristics of cotton fabrics, depending on the area of application, are described in the tables of GOST 29298-2005. In the production of clothing and fabrics, these parameters are adhered to, because these numbers are an indicator of quality.
What can be sewn from thick and thin cotton (cotton)
Various types of clothing and home textiles are made from cotton. Examples:
- chintz makes excellent shirts, beds, summer dresses, tablecloths;
- calico - dense, comfortable material, may include artificial fibers, suitable for curtains and linen;
- twisted cambric yarn is transparent and thin - an ideal raw material for underwear, dresses, blouses;
- veil - a thin, almost transparent material from which I sew veils, scarves, blouses, dresses, curtains, decor for hats;
- poplin is a material with a small transverse rib, it is obtained by weaving a thin warp with a coarse weft; beds, shirts, dresses, and pillow covers are made from poplin;
- taffeta - hard, dense textile, draped, used for sewing home textiles and clothing parts;
- denim – fabric for jackets, shirts, trousers;
When choosing a material for sewing, the optimal density and conditions of use must be taken into account.
Types by fabric type
- Costume ones - do not have stretchy properties unless spandex threads are added to their composition. They form part of natural cotton fabrics.
- Knitwear has stretch and is often used in clothing. Such materials include, for example, jersey and footer. May have a percentage of synthetic additives.
- Impregnated fabrics have additional properties, for example, fire-resistant or water-repellent. Some types of cotton products are treated with resins to reduce creasing.
Names of cotton fabrics
| Name | Description |
| Satin | Smooth shiny fabric with high density. Because of its shine, it is often compared to silk. Made from 100% cotton or polyester. |
| Percale | It is more often used for sewing bed linen, since the average density of this material is 115 g/m². Stronger than satin, although less thick. |
| Poplin | matte plain weave fabric. Often used in needlework for patchwork techniques, such as patchwork, due to the variety of color palettes. |
| Batiste | thin, translucent fabric. The most delicate type of cotton fabric. It is used to make not only clothes or bed linen, but also curtains. |
| Chintz | cheap material, known to everyone since childhood. It comes in a wide variety of colors and patterns and is made from 100% cotton. |
| Flannel | soft, dense fabric with pile, has a warming effect. Ideal for sewing adult and children's pajamas and diapers. |
| Footer | It has a smooth front side and a combed back side. To make the product stretch better, elastane is added to the composition in addition to cotton. |
| Kulirka | knitted fabric. To make the material more elastic, elastane is added to it. |
| Calico | 100% cotton fabric, plain weave. |
Care
- bleached cotton can withstand temperatures up to 95°C, the addition of bleaching agents is allowed;
- the temperature for washing colored cotton should not exceed 60°C;
- It is better to wash thin materials in cold or warm water (no more than 40 degrees);
- You should not use the drying mode in the washing machine, because this textile wrinkles a lot;
- you need to iron cotton through a wet cloth, then the process will be faster and more efficient;
- Before sewing from cotton materials, it is advisable to carry out decating to reduce further shrinkage.